California Wildfire Map: Your Essential Guide To Safety
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Golden State's Fiery Challenge
- Understanding California Wildfire Maps
- Types of Wildfire Maps and Data Sources
- The Human Element: Policies, Prevention, and Politics
- Impact of Wildfires Beyond the Flames
- Preparing for Wildfire Season: A Community Effort
- The Future of Wildfire Management and Mapping
- Navigating the Aftermath: Recovery and Resilience
- Conclusion
Introduction
California, a land often depicted as an endless panorama of sunshine, sprawling beaches, sophisticated urban dining, and ever-evolving shopping districts, truly offers a lifestyle many dream of. It's a place where, as the saying goes, "whatever you want to do, whatever you want to see, whatever life you want to live, you can find it here." From its historical role as the birthplace of two U.S. presidents, Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan, underscoring its pivotal national importance since the 1980s, to its current status as an economic powerhouse—boasting 554 pharmaceutical companies, far outstripping New Jersey and New York combined—California embodies innovation and opportunity.
Yet, beneath this veneer of perpetual summer and prosperity lies a stark reality: the increasing threat of devastating wildfires. These infernos, fueled by a combination of climate change, historical land management practices, and human activity, regularly cast a smoky pall over the Golden State, turning idyllic landscapes into scenes of destruction. For residents and emergency responders alike, understanding the dynamic and unpredictable nature of these fires is paramount. This is where the crucial tool of a **California wildfire map** comes into play, offering a lifeline of information in times of crisis.
The Golden State's Fiery Challenge
California's unique geography and climate make it inherently susceptible to wildfires. Its Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, creates ideal conditions for vegetation to dry out and become highly flammable. The state's diverse landscapes, from dense forests and chaparral to urban-wildland interfaces, provide ample fuel. Furthermore, the infamous Santa Ana and Diablo winds act as accelerants, fanning flames and spreading embers over vast distances at terrifying speeds.
The past few years have seen an alarming escalation in the frequency and intensity of these blazes. We've witnessed firsthand the consequences of long-term drought conditions, as seen in the devastating Parker fire in July of a recent dry year. Despite numerous warnings from researchers and scientists about the heightened risk of wildfires, the state continues to grapple with these catastrophic events. Even insurance companies, recognizing the escalating danger, have become increasingly wary, reflecting the profound financial and societal impact of these fires.
Understanding California Wildfire Maps
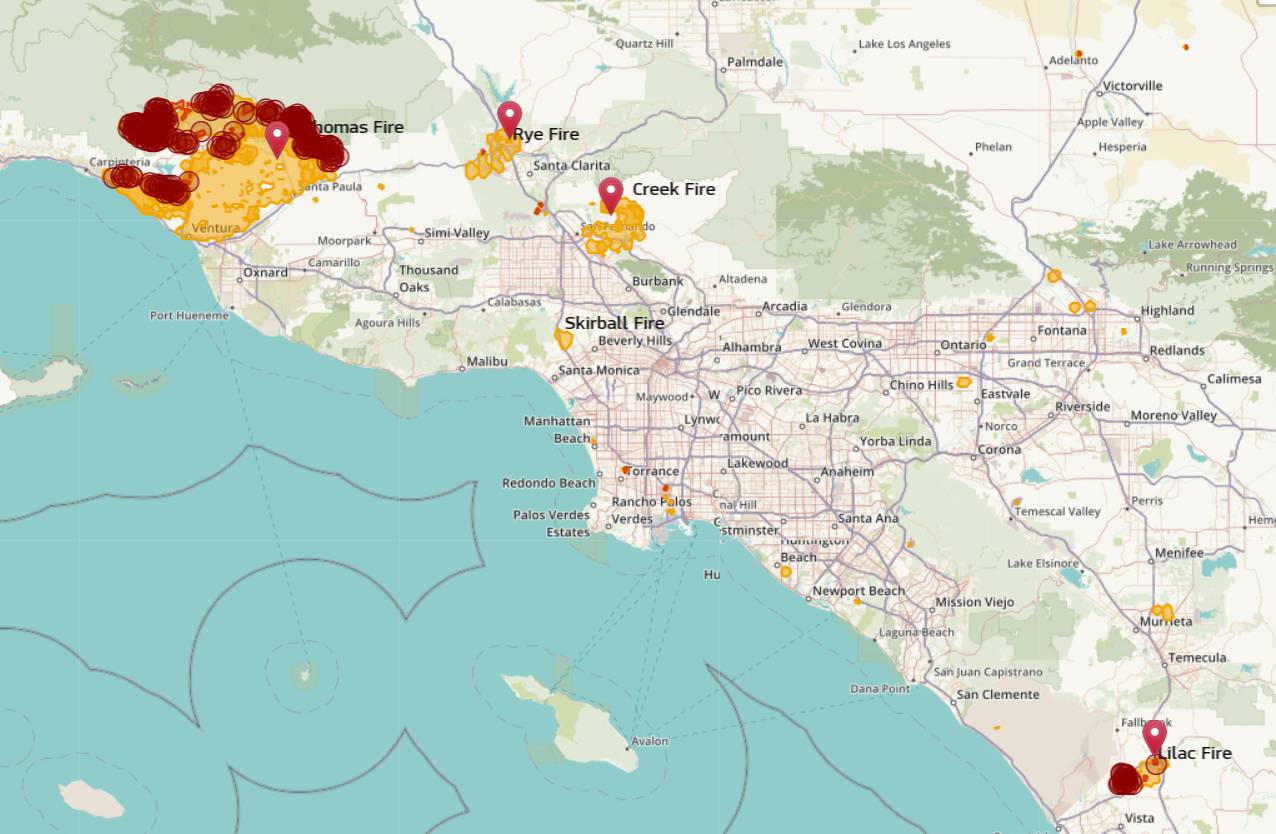
At their core, **California wildfire maps** are visual representations of active fires, their perimeters, and related critical information. They serve as indispensable tools for a wide array of users, from emergency services and firefighters to residents and concerned citizens. These maps provide real-time or near real-time data, allowing for informed decision-making regarding evacuations, resource allocation, and public safety.
A comprehensive wildfire map typically displays:
- Active Fire Locations: Pinpointing where fires are currently burning.
- Fire Perimeters: Showing the boundaries of contained and uncontained areas.
- Evacuation Zones: Clearly delineating areas under mandatory or advisory evacuation orders.
- Road Closures: Indicating impassable routes due to fire activity or emergency operations.
- Smoke Plumes and Air Quality: Often overlaid with data on smoke dispersion and air quality index (AQI).
- Weather Conditions: Including wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity, which are crucial for predicting fire behavior.
- Topography: Highlighting terrain features that influence fire spread.
- Emergency Shelters: Locations for displaced residents.
Types of Wildfire Maps and Data Sources
The data powering a **California wildfire map** comes from a variety of sophisticated sources, each contributing a piece to the larger puzzle of fire intelligence. These sources include:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with thermal sensors can detect heat signatures from fires, even through smoke, providing broad overviews of fire activity and spread. Agencies like NASA and NOAA are key providers of this raw data.
- Aircraft Surveillance: Manned aircraft and drones fly over active fires, capturing high-resolution images and infrared data that offer more detailed and localized information than satellites.
- Ground Crews and Incident Command: Firefighters on the ground provide crucial real-time updates on fire behavior, containment efforts, and damage assessments. This on-the-ground intelligence is vital for refining map data.
- Weather Stations: A network of weather stations across the state provides localized data on wind, temperature, and humidity, which are fed into fire prediction models.
- Public Reporting: While not a primary data source for official maps, initial reports from the public often alert authorities to new ignitions.
Key agencies and platforms that aggregate and disseminate this data include:
- Cal Fire (California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection): The primary state agency responsible for fire protection and resource management. Cal Fire's incident pages and interactive maps are often the most authoritative source for current fire information.
- National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC): Coordinates federal wildfire fighting resources and provides national fire information, including large incident maps.
- InciWeb: An interagency incident information system that provides detailed information on large wildfires, including maps, updates, and photos.
- NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration): Provides weather forecasts and satellite imagery crucial for fire prediction.
- Various Local Emergency Services: County and city emergency management agencies often provide localized maps and alerts specific to their jurisdictions.
Real-Time Tracking: How Maps Keep You Informed
The concept of "real-time" is critical when discussing a **California wildfire map**. Fire behavior can change in minutes, making up-to-the-minute information essential for safety. Modern mapping technologies leverage geographic information systems (GIS) to integrate data from multiple sources, constantly updating the map display. This allows users to see fire perimeters expand or contract, new ignitions appear, and evacuation orders change almost as they happen.
Many platforms offer interactive features, allowing users to zoom in on specific areas, search for addresses, and even receive personalized alerts. This dynamic nature ensures that the public has access to the most current and accurate information, empowering them to make timely decisions about their safety and property.
The Human Element: Policies, Prevention, and Politics
While natural factors play a significant role, human decisions—or the lack thereof—are increasingly recognized as major contributors to California's wildfire crisis. This includes land management policies, urban planning, and the political will to implement effective prevention strategies. The discussion around wildfires often becomes entangled in political debates, reflecting differing views on environmental protection, economic development, and government responsibility.
Land Management and Fuel Reduction
One critical aspect of wildfire prevention is land management, particularly fuel reduction. Decades of fire suppression, while initially intended to protect communities, have led to an unnatural buildup of dense vegetation and dead organic matter in forests and wildlands. This "fuel load" creates conditions for more intense and destructive fires when they do occur.
There's a significant debate around the balance between environmental protection and proactive land management. Critics, including figures like former President Trump, have pointed to California's environmental policies, suggesting they contribute to the problem by limiting water storage and hindering the clearing of dead trees and leaves. While environmental concerns are valid, the scientific consensus increasingly points to the necessity of active forest management, including prescribed burns and mechanical thinning, to reduce fuel loads and restore ecological balance. The warnings from numerous researchers about high wildfire risk due to long-term dryness and accumulated fuel have been consistent, even terrifying insurance companies with the scale of potential losses.
The Political Landscape of Fire Management
The governance of California, often characterized by its "Democratic extreme-left rule" by some critics, faces immense pressure to address the wildfire crisis. The state's political landscape, while not exhibiting the "resolve to bring down the federal government" seen in historical Southern conflicts, certainly sees its share of intense debate. California's struggle against wildfires is not merely an environmental one; it's deeply political, involving complex decisions about funding for fire services, land use regulations, and climate change policies. The state's citizens, largely through the ballot box, continue to push for solutions, though the tools of political struggle remain largely confined to existing institutional frameworks.
Finding common ground between various stakeholders—environmentalists, developers, agricultural interests, and local communities—is a monumental challenge. Policies related to building codes in high-risk areas, utility infrastructure upgrades (as power lines are often ignition sources), and funding for fire-safe communities are constantly under review and subject to political contention. The effectiveness of any **California wildfire map** as a safety tool is intrinsically linked to the policies that dictate land use, prevention efforts, and emergency response capabilities.
Impact of Wildfires Beyond the Flames
The consequences of California's wildfires extend far beyond the immediate destruction of homes and natural landscapes. The economic toll is immense, encompassing property damage, business interruption, and the high cost of suppression efforts. Industries, including the state's dominant pharmaceutical sector—which, with 554 companies, is the nation's largest—can be indirectly affected by disruptions to supply chains, labor availability, and overall economic stability, though many are concentrated in less fire-prone urban centers.
Tourism, a vital part of California's economy, also suffers. While attractions like Legoland California in Carlsbad might be geographically removed from major fire zones, the general perception of a state constantly battling blazes can deter visitors. The picturesque image of endless sunshine and ocean views is frequently overshadowed by smoky skies and news of evacuations, impacting the very allure that draws people to California.
Beyond economics, the human cost is profound. Wildfires lead to displacement, loss of life, and significant health impacts from smoke inhalation, which can travel hundreds of miles. The psychological trauma experienced by those who lose their homes, or live in constant fear of the next fire, is immeasurable. The long-term environmental damage includes soil erosion, water contamination, and habitat destruction, further exacerbating ecological challenges.
Preparing for Wildfire Season: A Community Effort
Given the persistent threat, preparedness is no longer optional for Californians; it's a way of life. Individual actions, combined with community-level initiatives, are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring safety. This includes creating defensible space around homes, hardening structures against embers, and having a comprehensive emergency plan.
Key steps for preparedness include:
- Creating Defensible Space: Clearing flammable vegetation within 100 feet of structures.
- Home Hardening: Using fire-resistant materials for roofs, vents, and siding.
- Emergency Kit: Assembling supplies including food, water, medications, and important documents.
- Communication Plan: Establishing how family members will communicate and where they will meet.
- Staying Informed: Regularly checking official sources for fire updates and alerts, especially a reliable **California wildfire map**.
Evacuation Planning: Using Maps for Safety
Perhaps the most critical application of a **California wildfire map** for residents is during evacuation planning. These maps clearly delineate evacuation zones (e.g., Zone A, Zone B) and show designated evacuation routes. Before a fire even threatens, residents should familiarize themselves with these maps, identifying primary and secondary escape routes from their homes and neighborhoods.
During an active fire, regularly consulting the most current wildfire map is essential for understanding evacuation orders and avoiding areas of active fire or road closures. Many mapping applications also integrate real-time traffic data, helping evacuees choose the safest and most efficient routes. This proactive engagement with mapping tools can literally be the difference between life and death, allowing individuals to evacuate safely and avoid being trapped by fast-moving flames.
The Future of Wildfire Management and Mapping
The battle against California's wildfires is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of fire science. The future of wildfire management will increasingly rely on sophisticated data analytics, artificial intelligence, and advanced mapping capabilities.
- Predictive Modeling: AI and machine learning are being used to analyze vast datasets (weather, topography, fuel loads) to predict fire behavior with greater accuracy, allowing for more strategic resource deployment.
- Enhanced Sensor Technology: New generations of satellites, drones, and ground sensors will provide even more granular and real-time data for **California wildfire maps**, improving situational awareness for firefighters and the public.
- Integrated Systems: Efforts are underway to create more seamless integration between various data sources and emergency response systems, ensuring that information flows efficiently from detection to public alert.
- Community Resilience Planning: Maps will play a larger role in long-term community planning, identifying high-risk areas for development, planning fuel breaks, and designing evacuation infrastructure.
- Climate Change Adaptation: As climate change continues to influence fire seasons, mapping tools will be crucial for understanding shifting risk profiles and adapting land management and emergency response strategies accordingly.
These technological advancements, coupled with ongoing research into fire ecology and human behavior, offer hope for more effective wildfire management in the years to come, though the underlying challenges of a changing climate and human development in fire-prone areas remain formidable.
Navigating the Aftermath: Recovery and Resilience
Once the flames subside, the long and arduous process of recovery begins. This phase involves not only physical rebuilding but also emotional healing and environmental restoration. **California wildfire maps** continue to be relevant in the aftermath, albeit in a different capacity.
- Damage Assessment Maps: These maps delineate areas of destruction, helping authorities assess the extent of damage to infrastructure, homes, and natural resources.
- Hazard Maps: Post-fire landscapes are prone to new hazards like mudslides and debris flows, especially after rainfall. Maps can identify high-risk areas for these secondary disasters, guiding recovery efforts and informing residents.
- Rebuilding and Permitting Maps: Local governments use maps to manage rebuilding efforts, showing areas where permits are being issued and tracking progress.
- Environmental Restoration Maps: Conservationists and land managers use maps to plan and monitor reforestation, erosion control, and habitat restoration projects.
The resilience of California's communities is tested year after year, but through collective effort, informed planning, and the strategic use of mapping technologies, the state strives to rebuild stronger and more fire-adapted.
Conclusion
California, a state of unparalleled beauty and opportunity, also faces the relentless challenge of wildfires. From the political debates surrounding land management to the very real threat to homes and lives, these fires touch every aspect of the Golden State. In this complex and often terrifying landscape, the **California wildfire map** emerges as an indispensable tool—a beacon of information guiding residents, firefighters, and policymakers alike.
Understanding how to read and utilize these maps is no longer a niche skill but a fundamental aspect of living safely in California. As we move forward, the integration of advanced mapping technologies, coupled with proactive land management and community preparedness, will be crucial in mitigating the impact of future fire seasons. Stay informed, prepare diligently, and always consult official wildfire maps during fire season. Your safety, and the safety of your community, depends on it. Share this article to help spread awareness, and explore other resources on our site for more tips on wildfire preparedness and community resilience.

一文看懂,为什么加州大火令人绝望?_百科TA说
NASA公布了加州山火高清卫星照 烟尘蔓延至加州海岸|NASA|公布-滚动读报-川北在线
加州圣迭戈地图,美圣迭戈,圣迭戈(第5页)_大山谷图库